5G Technology Is Coming To Lebanon – What You Need To Know

Global mobile data traffic is expected to reach 49 exabytes per month by 2021 at a compound annual growth rate of 47 percent. The current generation of wireless networks isn’t able to handle such massive growth, driven in part by everyday mobile activities such as web browsing, audio and video streaming, and mobile gaming (I see you PUBG players), but also by various connected industries. The next generation of wireless networks – 5G technology – is supposed to enable connectivity at a massive scale and bring us a world where billions of devices transmit data at super-fast speeds, with minimal latency, and with near-perfect availability.

At the moment, telecom companies, industry groups, and hardware manufacturers are all working together to prepare the first commercial 5G networks for their public debut in the early 2020s, and Lebanon is one of the countries where 5G is expected to have the biggest impact.
5G In A Nutshell
It’s easy to see 5G as not much more than a faster version of today’s 4G. Headlines often mention that 5G networks should be able to achieve a peak data rate of 20 Gbps, which would make 5G networks more than 100x faster than 4G networks, whose peak data rate reaches only around 100 Mbps.
In reality, 5G is about much more than speed improvements. The objective of the technology is to enable new use cases in all areas of our daily lives by laying down the infrastructure of a massive network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other internet-connected items, called the Internet of Things (IoT).
“Simply, the Internet of Things is made up of devices – from simple sensors to smartphones and wearables – connected together,” says Matthew Evans, the IoT program head at techUK. “IoT offers us the opportunity to be more efficient in how we do things, saving us time, money and often emissions in the process,” he adds.
Beyond improved data transfer speeds, IoT and critical communication use cases will require new types of improved performance which are only possible if 5G meets certain specification requirements, namely:
- Up to 20 Gbps data rate.
- Latency of just 1-millisecond.
- Capacity for 10-100x number of connections.
- 99.9 percent availability.
- 100 percent coverage.
- 90 percent reduction in network energy usage.
- Up to 10-year battery life for low-power IoT devices.
To achieve this, 5G networks will rely on a whole host of new technologies, including millimeter waves, small cells, massive MIMO, and beamforming, just to name some of the most prominent ones.
- Millimeter Waves: If you’ve ever tried to set up a WiFi network in a crowded urban area, you probably know quite well how crammed the radio-frequency spectrum is. One way how to get around this and achieve higher data transfer speeds with less dropped connections is to broadcast on a new range of the spectrum. For 5G, wireless engineers have decided to use frequencies between 30 and 300 gigahertz, called millimeter waves because they vary in length from 1 to 10 mm. Because of how short the waves are, they have a hard time penetrating trees, buildings, and other solid objects, which is where the next technology comes in.
- Small Cells: 4G networks rely on high-power cell towers that transmit signals over long ranges. 5G networks will rely on densely placed portable miniature base stations with minimal power requirements. It’s expected that there will be hundreds and even thousands of these base stations in every city, placed roughly every 250 meters. Each 5G base stations will be equipped with multiple antennas to take advantages of another new technology: massive MIMO.
- Massive MIMO: You may already be familiar with MIMO (Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) from your home router. MIMO is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmit and receive antennas, and 5G takes it to the next level by featuring dozens of antennas on a single array, increasing the capacity of mobile networks by a factor of 22 or greater.
- Beamforming: To prevent 5G base stations and their numerous antennas from causing an Armageddon of interference, 5G uses a technology called beamforming to efficiently direct traffic to a particular user. Again, beamforming is already used by many Wi-Fi routers, but it has never been applied at such a massive scale before.
Real-Life Applications Of 5G
At the Mobile World Congress 2018 in Spain, telecom and tech companies demonstrated the wide range of use cases enabled by 5G and talked at length about how 5G will bring new opportunities for people, society, and businesses.
High-end smartphones have been able to record 4K videos for a long time, but the capacity of the current 4G networks is not sufficient for lag-free 4K streaming. With 5G, it will finally be possible to stream 4K videos even when not on WiFi. 5G is also expected to usher in the era of 8K video streaming, which would make live virtual reality events much more attractive than they are today.
“After all, 5G will have data rates capable of sending such information out and back to a remote location, thereby eliminating the need for the VR player to own a top-of-the-line computer. And 5G could certainly reduce the lag that causes VR sickness by updating the headset on what it should display more quickly after you turn your head,” writes Michael Koziol, an associate editor at IEEE Spectrum.
Self-driving cars are another great example of a technology that can greatly benefit from extremely fast, low-latency connections. When it comes to the IoT and various internet-connected sensors and appliances, speed and latency are not as important. What is important, however, includes availability, security, and low energy usage, and 5G meets these criteria as well.
Role Of 5G In Lebanon
At the 10th annual Telecom Review Summit held in Lebanon on April 13th, Alfa, one of the two mobile network operators in Lebanon, became the first Lebanese operator to achieve an integrated 5G live experience.
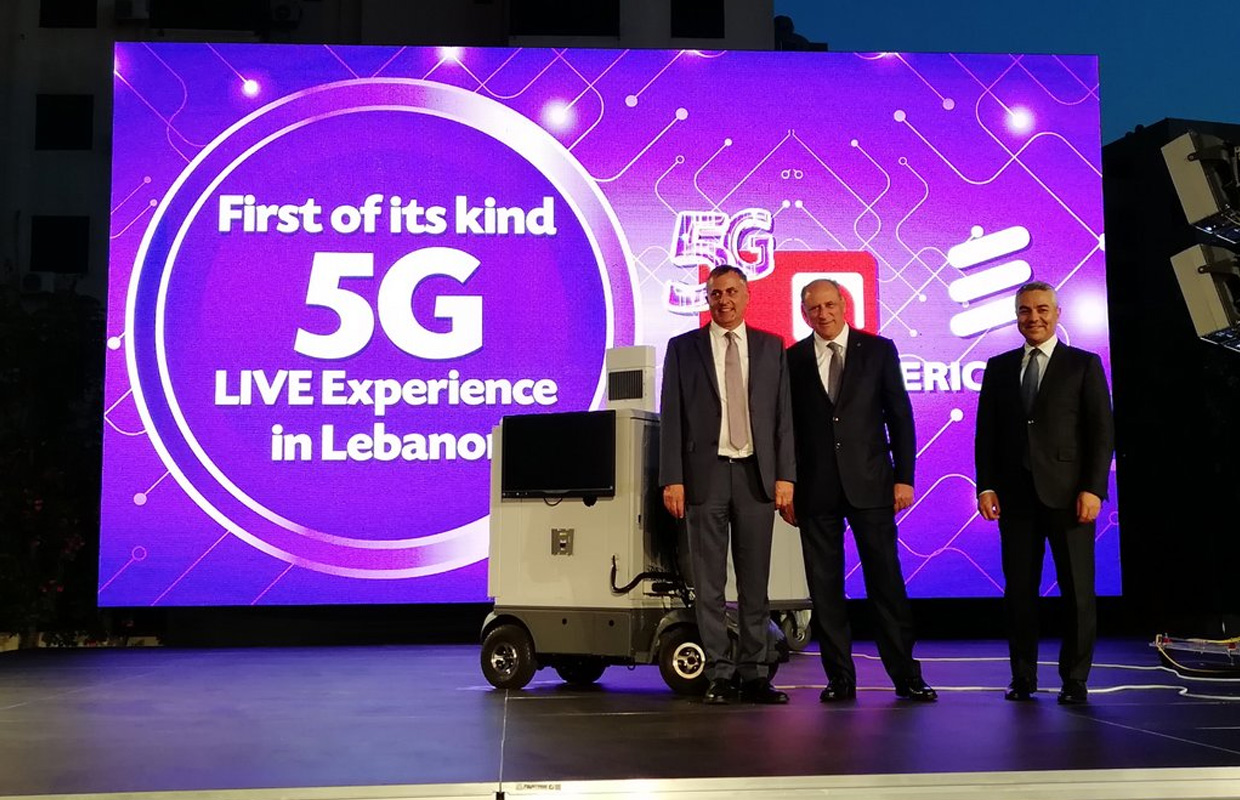
“This event in which we witness for the first time in Lebanon the 5G capabilities, confirms Alfa’s readiness to introduce the 5G technology,” said Alfa CEO and Chairman Marwan Hayek. “5G will have a huge impact on the economy for the next 15 years, with global GDP expected to grow by 2.9 percent, and 5G contributing to 0.2 percent of this GDP. It will also create 22 million new jobs globally, most of which are new jobs, hence the primary role of the educational sector and educational institutions is to educate the young generation on the specialties in demand.”
Touch, the other mobile network operator in Lebanon, successfully demonstrated its 5G network at the Grand Serail in September, achieving an impressive data transfer speed of 1560 Mbps on the commercial C-Band spectrum and demonstrating a simultaneous playback of sixteen 4K videos on the same network.

“At the Ministry of Telecommunications, we are determined to modernize the existing infrastructure to accommodate the latest technology advancements. So we began to deploy fiber optics across Lebanon, to benefit the Lebanese citizens with modern technology, in addition to expanding mobile networks to keep up with developments,” said Caretaker Minister of Telecommunications Jamal Jarrah at the event.
Clearly, Lebanon is on the right track to become one of the first countries in the world to build a robust 5G infrastructure, and that’s great news for the country’s thriving startup scene as well as its struggling economy.
TL;DR
5G is the fifth generation of cellular mobile communications, and it’s expected to enable countless novel use cases across many industries, including 8K video streaming, virtual reality, self-driving cars, and the Internet of Things. Even though telecom companies, industry groups, and hardware manufacturers are still finalizing 5G specifications, some countries, including Lebanon, are already preparing for large-scale 5G adoption, knowing that it will likely drive economic growth and foster innovation.













 © 2024
© 2024
1 Comment